KLEEMANN blow bars for impact crushers
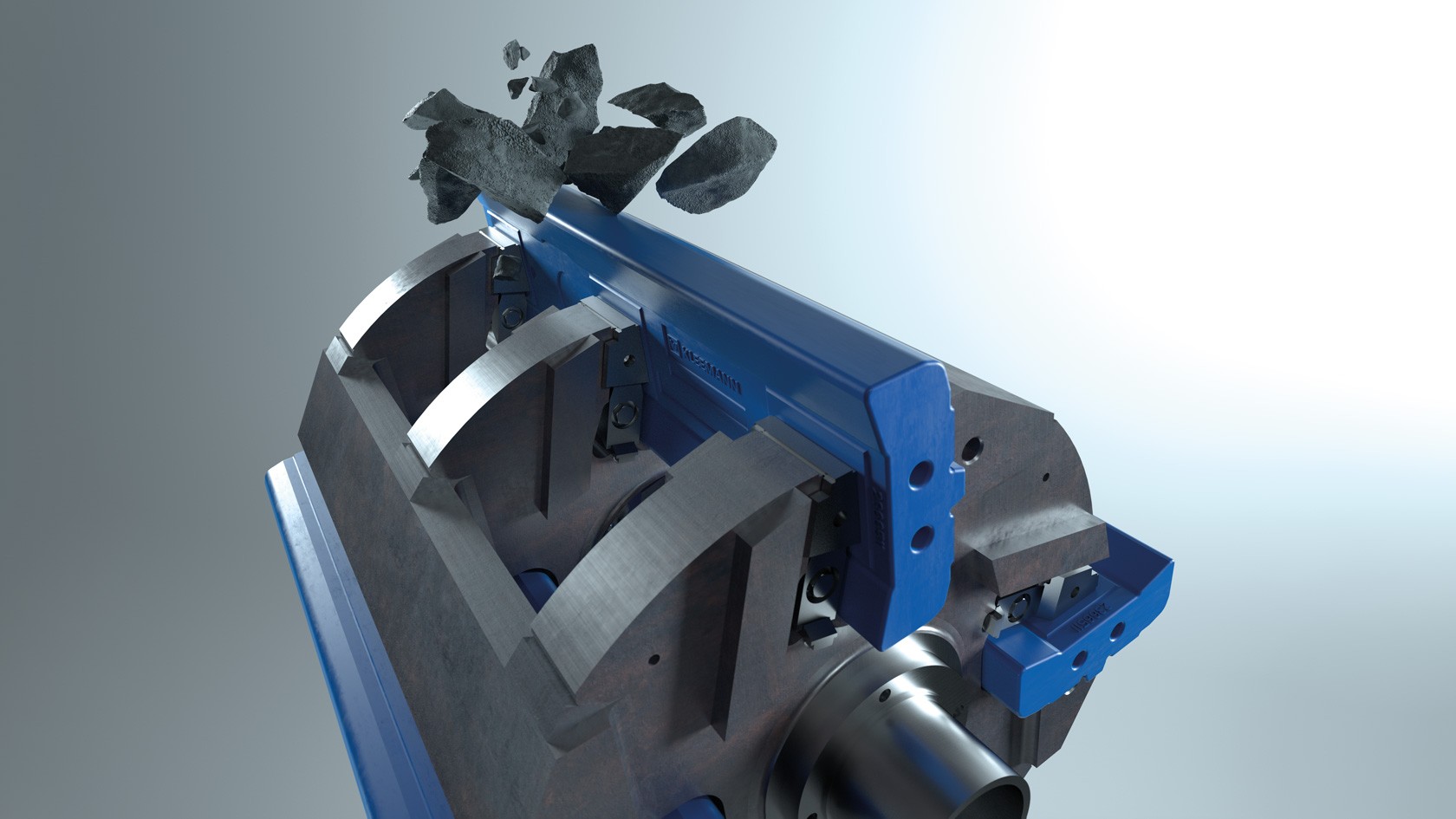

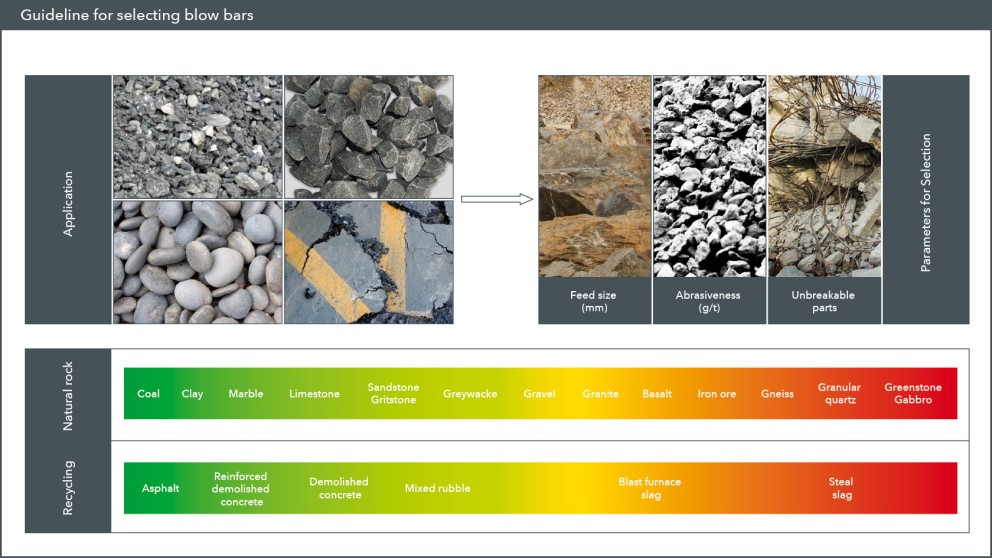
KLEEMANN impact crushers can be used for a wide range of applications. From classical processing of natural stone and the recycling of high volumes of building rubble to quarrying and mining applications – the focus is always on two particular challenges: increasing utilization rates and lowering operating costs. The crushing tools are subject to varying degrees of wear depending on various influencing factors.
Genuine KLEEMANN blow bars offer much more than just the right sizes. The materials used, alloying elements and the entire casting process are important foundations for a reliable crushing tool. KLEEMANN impact crushers can be used for a wide range of applications. From classical processing of natural stone and the recycling of high volumes of building rubble to quarrying and mining applications – the focus is always on two particular challenges: Increasing the service life of blow bars and lowering operating costs.
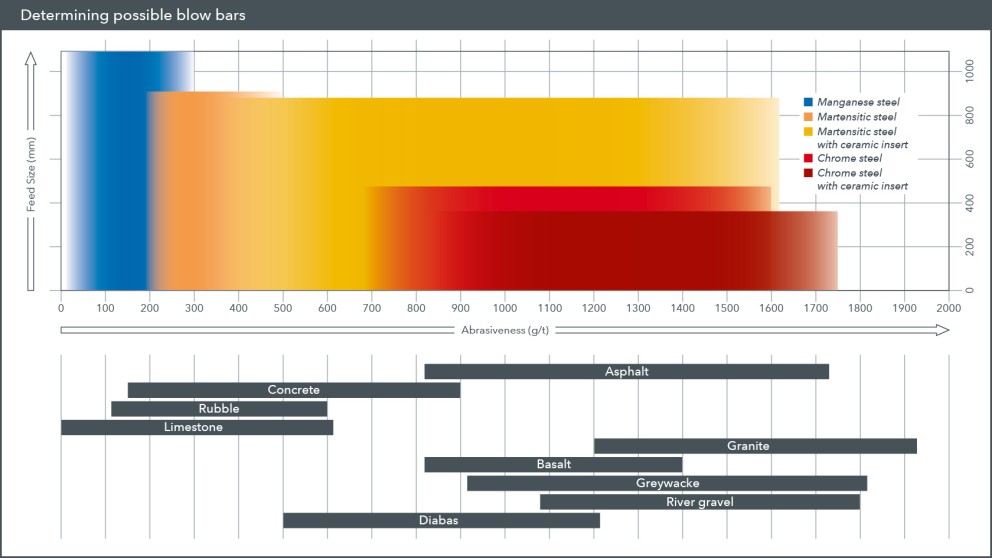
The cost-effective usage of blow bars is influenced by a number of factors. e.g. the feed material, rotor speed, moisture content, feed size and the crushing ratio. Determine the ideal blow bar for your specific application with the aid of the following points. Access a choice of various different blow bars and begin your crushing project with economically optimised crushing tools.
| Version | Material | Kleemann designation | Properties | Recommended applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Monolithic blow bars | Manganese steel | TRON.Mn | Manganese steel is used when high impact resistance and elasticity are essential prerequisites. Sufficiently high impact force consolidates the manganese steel of the blow bar (cold consolidation) and thus reduces wear. | |
| Martensitic steel | TRON.M | This steel unites hardness and impact resistance for cases where the use of chrome steel would lead to breakage. Furthermore, martensitic steel blow bars have a longer service life than manganese steel blow bars when processing abrasive materials. | ||
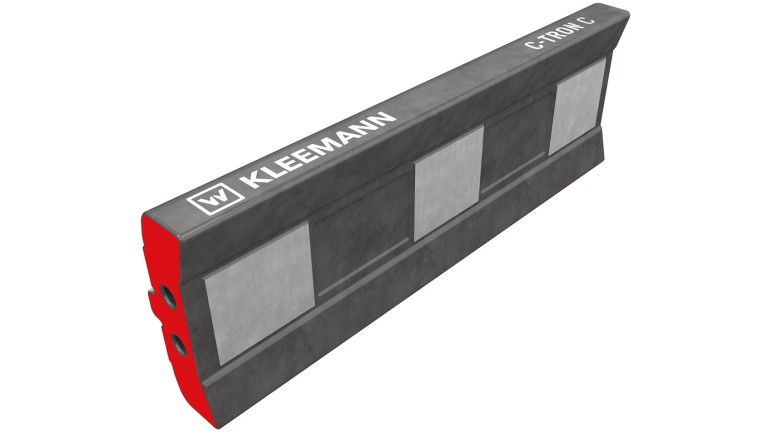
| Chrome steel | TRON.C | Chrome steel is characterised in particular by its extreme hardness and has the advantage of being particularly wear resistant. Chrome steel is the best choice for applications where manganese steel or martensitic steel blow bars would wear out too quickly. | ||
| Metal matrix composites | Martensitic steel with ceramic insert | TRON.MC | The blow bar consist of a martensitic steel body internally reinforced with ceramic inserts. This composite material combines the hardness of ceramics with the mechanical properties of steel and has a 2 to 4 times longer service life compared to blow bars made from single alloys. | |
| TRON.MC+ | The cast ceramic insert is deeper and more elongated. This ensures that the impact edge remains intact until completely worn down, extending the service life compared to conventional MartComp/MartXpert blow bars for abrasive applications. | |||
| Chrome steel with ceramic insert | TRON.CC | The combination of the chrome steel body and ceramic inserts ensures a constant wear profile when processing highly abrasive pre-crushed materials as encountered especially in gravel pits and quarries. |
The correct assessment of blow bar wear is a prerequisite for the cost-effective operation of an impact crushing plant. Replacing blow bars at the right time guarantees successful operations and significantly reduces operating costs. It is common for blow bars not to wear evenly across their full width. The wear limit is reached when the specified minimum wear dimension is no longer fulfilled at any one point on the blow bar.
Please note that changing the blow bars too late will lead to increased wear on the rotor and the blow bar mountings. The consequences of this are costly subsequent damage and prolonged machine downtimes. Apart from the necessary renewal of the rotor armouring (hard facing), the clamping wedges for blow bar mounting are frequently also damaged.